Feb 04, 2020 Right Scheme for SSD. You have to select the right Scheme for the disk partition when you erase the disk. There are three options available to select the scheme and let see some details. GUID Partition Map: This is the usual format used for the non-start up discs in Mac with Intel processor. We are going to select this as the scheme for our. To partition and format a disk in OS X, you generally open Disk Utility, select the disk in the tool's sidebar, and click use the Partition tab to select and apply a partition scheme; however. In that case, choose Master Boot Record for the Scheme. Click Erase, and Disk Utility will erase and format the drive. Partitioning a Drive. You may want to divide a drive into more than one partition. When you do this, each partition is a volume, and each volume shows up as a separate drive on your Mac. Partition Magic a reliable partition manager for Mac is geared with all those features which are needed for the safety and security of your drive. With Partition Magic you can mix or resize the partitions, it lets you arrange data, create storage space, modify or edit partitions, perform multitasking, preview, and delete. There are also some paid-for alternatives with advanced features, see Best disk partition software for Mac for advice. Before you start, you should back up the drive you intend to partition, you.
- Best Mac Scheme Partition Software
- Change Partition Scheme Mac
- How To Check Partition Scheme
- Best Mac Scheme Partition Shortcut
- Best Mac Scheme Partition Software
Disk Utility User Guide
Partitioning a disk divides it into individual sections known as containers.
However, with APFS, you shouldn’t partition your disk in most cases. Instead, create multiple APFS volumes within a single partition. With the flexible space management provided by APFS, you can even install another version of macOS on an APFS volume.
Important: If you’re partitioning your internal physical disk because you want to install Windows, use Boot Camp Assistant instead. Do not use Disk Utility to remove a partition that was created using Boot Camp Assistant. Instead, use Boot Camp Assistant to remove the partition from your Mac.
Add a partition
Important: As a precaution, it’s best to back up your data before creating new partitions on your device.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, select a volume in the sidebar, then click the Partition button in the toolbar.
If Disk Utility isn’t open, click the Launchpad icon in the Dock, type Disk Utility in the Search field, then click the Disk Utility icon .
If you have multiple storage devices connected to your Mac, make sure you select a volume that’s on the device you want to partition.
When you select a volume that already has data on it, the pie chart shows a shaded area representing the amount of data on the volume and an unshaded area representing the amount of free space available for another volume. Disk Utility also shows whether the volume can be removed or resized.
Note: If you see a small volume with an asterisk, the partition is smaller than can be represented at the correct scale in the chart.
Read the information in the Apple File System Space Sharing dialog, then click Partition.
Click the Add button below the pie chart.
Type a name for the volume in the Name field.
For MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT volumes, the maximum length for the volume name is 11 characters.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose a file system format.
Enter the size or drag the resize control to increase or decrease the size of the volume.
Hacker voucher pulsa. Click Apply.
Read the information in the Partition Device dialog, then click Partition.
After the operation finishes, click Done.

After you partition a storage device, an icon for each volume appears in both the Disk Utility sidebar and the Finder sidebar.
Delete a partition
Best Mac Scheme Partition Software
WARNING: When you delete a partition, all the data on it is erased. Be sure to back up your data before you begin.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, select a volume in the sidebar, then click the Partition button in the toolbar.
If Disk Utility isn’t open, click the Launchpad icon in the Dock, type Disk Utility in the Search field, then click the Disk Utility icon .
In the Apple File System Space Sharing dialog, click Partition.
In the pie chart, click the partition you want to delete, then click the Delete button .
If the Delete button is dimmed, you can’t delete the selected partition.
Click Apply.
Read the information in the Partition Device dialog, then click Partition.
After the operation finishes, click Done.
Erase a partition


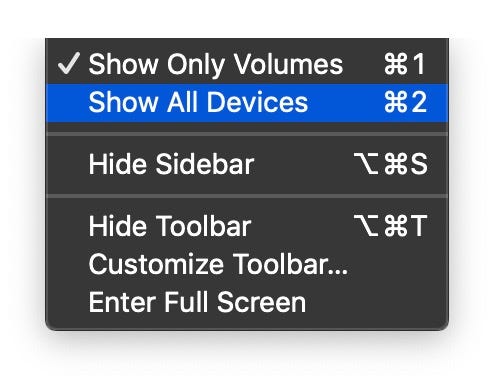
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose View > Show All Devices, then select the container you want to erase in the sidebar.
If Disk Utility isn’t open, click the Launchpad icon in the Dock, type Disk Utility in the Search field, then click the Disk Utility icon .
Click the Erase button in the toolbar.
If the Erase button is dimmed, you can’t erase the selected container.
Type a name for the volume in the Name field.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose a file system format.
After the operation finishes, click Done.
Change Partition Scheme Mac
Enlarge a partition on a storage device
How To Check Partition Scheme
If you have multiple partitions on a device and one of them is running out of space, you may be able to enlarge it without losing any of the files on it.
Best Mac Scheme Partition Shortcut
To enlarge a volume, you must delete the volume that comes after it on the device, then move the end point of the volume you want to enlarge into the freed space. You can’t enlarge the last volume on a device.
Best Mac Scheme Partition Software
WARNING: When you delete a volume or partition, all the data on it is erased. Be sure to back up your data before you begin.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, select a volume in the sidebar, then click the Partition button .
If Disk Utility isn’t open, click the Launchpad icon in the Dock, type Disk Utility in the Search field, then click the Disk Utility icon .
In the Apple File System Space Sharing dialog, click Partition.
In the pie chart, select the partition you want to delete, then click the Delete button .
If the Delete button is dimmed, you can’t delete the selected partition.
Click Apply.
Read the information in the Partition Device dialog, then click Partition.
After the operation finishes, click Done.
- A swap partition (at least 256 MB) — swap partitions are used to support virtual memory. In other words, data is written to a swap partition when there is not enough RAM to store the data your system is processing.In years past, the recommended amount of swap space increased linearly with the amount of RAM in the system. But because the amount of memory in modern systems has increased into the hundreds of gigabytes, it is now recognized that the amount of swap space that a system needs is a function of the memory workload running on that system. However, given that swap space is usually designated at install time, and that it can be difficult to determine beforehand the memory workload of a system, we recommend determining system swap using the following table.
Amount of RAM in the System Recommended Amount of Swap Space 4GB of RAM or less a minimum of 2GB of swap space 4GB to 16GB of RAM a minimum of 4GB of swap space 16GB to 64GB of RAM a minimum of 8GB of swap space 64GB to 256GB of RAM a minimum of 16GB of swap space 256GB to 512GB of RAM a minimum of 32GB of swap space Table 7.3. Recommended System Swap Space
Note that you can obtain better performance by distributing swap space over multiple storage devices, particularly on systems with fast drives, controllers, and interfaces. A
The partition mounted on/boot/partition (250 MB)/boot/contains the operating system kernel (which allows your system to boot Fedora), along with files used during the bootstrap process. For most users, a 250 MB boot partition is sufficient.Btrfs
The GRUB bootloader does not support the Btrfs file system. You cannot use a btrfs partition for/boot.Note
If your hard drive is more than 1024 cylinders (and your system was manufactured more than two years ago), you may need to create a/boot/partition if you want the/(root) partition to use all of the remaining space on your hard drive.Note
If you have a RAID card, be aware that some BIOSes do not support booting from the RAID card. In cases such as these, the/boot/partition must be created on a partition outside of the RAID array, such as on a separate hard drive.A
This is where 'rootpartition (3.0 GB - 5.0 GB)/' (the root directory) is located. In this setup, all files (except those stored in/boot) are on the root partition.A 3.0 GB partition allows you to install a minimal installation, while a 5.0 GB root partition lets you perform a full installation, choosing all package groups.Root and
/rootThe/(or root) partition is the top of the directory structure. The/rootdirectory (sometimes pronounced 'slash-root') directory is the home directory of the user account for system administration.